AuthenticationFlowError = Java.type("org.keycloak.authentication.AuthenticationFlowError");
function authenticate(context) {
LOG.info(script.name + " --> trace auth for: " + user.username);
if ( user.username === "tester"
&& user.getAttribute("someAttribute")
&& user.getAttribute("someAttribute").contains("someValue")) {
context.failure(AuthenticationFlowError.INVALID_USER);
return;
}
context.success();
}Authentication Flows
An authentication flow is a container for all authentications, screens, and actions that must happen during login, registration, and other
Keycloak workflows.
If you go to the admin console Authentication left menu item and go to the Flows tab, you can view all the defined flows
in the system and what actions and checks each flow requires. This section does a walk through of the browser login flow. In the
left drop down list select browser to come to the screen shown below:
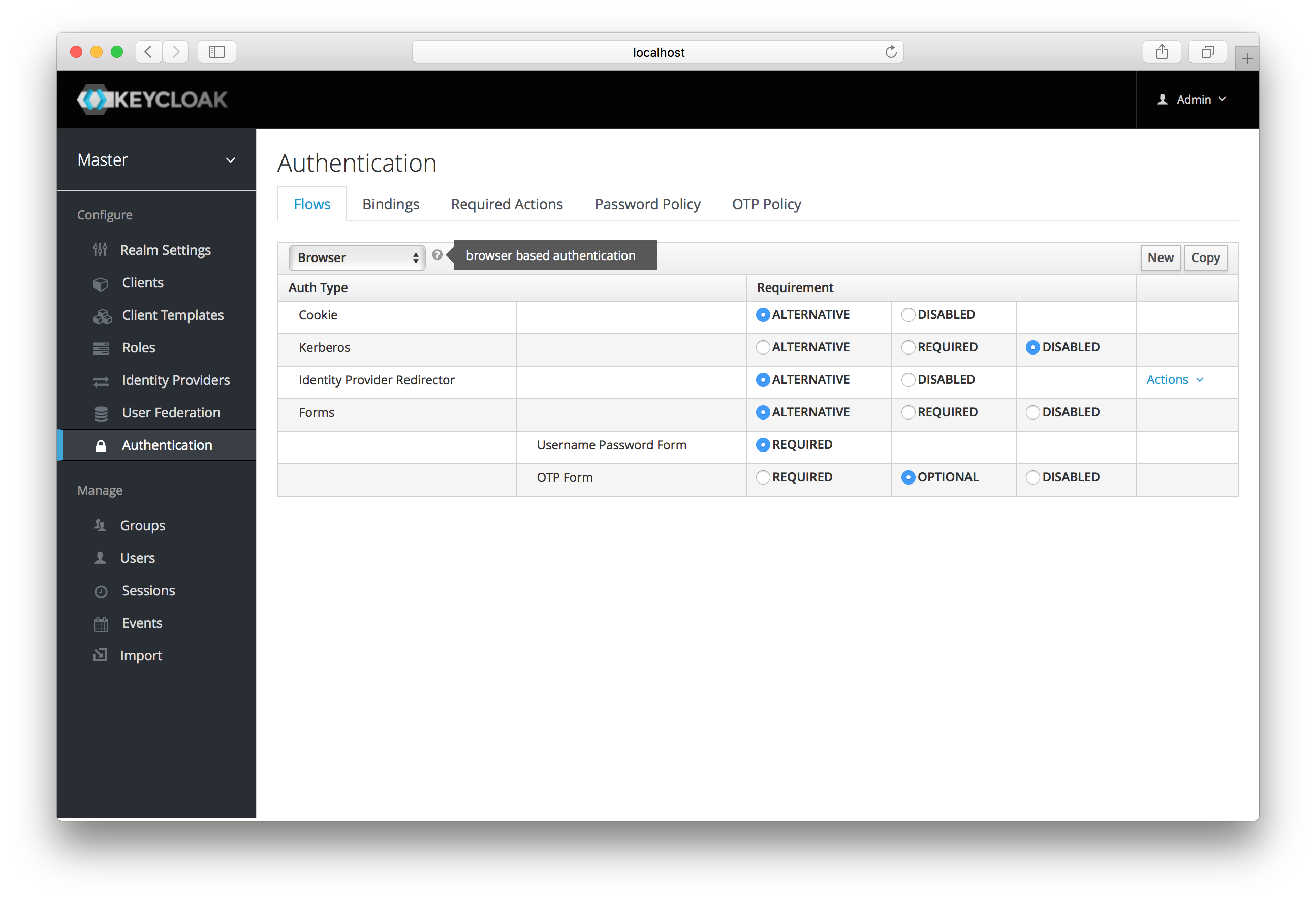
If you hover over the tooltip (the tiny question mark) to the right of the flow selection list, this will describe what the flow is and does.
The Auth Type column is the name of authentication or action that will be executed. If an authentication is indented
this means it is in a sub-flow and may or may not be executed depending on the behavior of its parent. The Requirement
column is a set of radio buttons which define whether or not the action will execute. Let’s describe what each radio
button means:
- Required
-
This authentication execution must execute successfully. If the user doesn’t have that type of authentication mechanism configured and there is a required action associated with that authentication type, then a required action will be attached to that account. For example, if you switch
OTP FormtoRequired, users that don’t have an OTP generator configured will be asked to do so. - Optional
-
If the user has the authentication type configured, it will be executed. Otherwise, it will be ignored.
- Disabled
-
If disabled, the authentication type is not executed.
- Alternative
-
This means that at least one alternative authentication type must execute successfully at that level of the flow.
This is better described in an example. Let’s walk through the browser authentication flow.
-
The first authentication type is
Cookie. When a user successfully logs in for the first time, a session cookie is set. If this cookie has already been set, then this authentication type is successful. Since the cookie provider returned success and each execution at this level of the flow is alternative, no other execution is executed and this results in a successful login. -
Next the flow looks at the Kerberos execution. This authenticator is disabled by default and will be skipped.
-
The next execution is a subflow called Forms. Since this subflow is marked as alternative it will not be executed if the
Cookieauthentication type passed. This subflow contains additional authentication type that needs to be executed. The executions for this subflow are loaded and the same processing logic occurs -
The first execution in the Forms subflow is the Username Password Form. This authentication type renders the username and password page. It is marked as required so the user must enter in a valid username and password.
-
The next execution is the OTP Form. This is marked as optional. If the user has OTP set up, then this authentication type must run and be successful. If the user doesn’t have OTP set up, this authentication type is ignored.
Executions
Executions can be used
A script authenticator allows to define custom authentication logic via JavaScript.
Custom authenticators. Authentication scripts must at least provide one of the following functions:
authenticate(..) which is called from Authenticator#authenticate(AuthenticationFlowContext)
action(..) which is called from Authenticator#action(AuthenticationFlowContext)
Custom Authenticator’s should at least provide the `authenticate(..) function.
The following script javax.script.Bindings are available for convenient use within script code.
script-
the
ScriptModelto access script metadata realm-
the
RealmModel user-
the current
UserModel session-
the active
KeycloakSession authenticationSession-
the current
AuthenticationSessionModel httpRequest-
the current
org.jboss.resteasy.spi.HttpRequest LOG-
a
org.jboss.logging.Loggerscoped toScriptBasedAuthenticator
Note that additional context information can be extracted from the context argument passed
to the authenticate(context) action(context) function.